The document Bill Of Lading is very important and common to importers and exporters. However, upon the popularity of this document, the majority still did not have a better understanding of it. Meanwhile, in this article, you will learn about the meaning, types, purpose, and other necessary information about the Bill of lading.
What Is the Meaning of Bill of Lading

Another name for a bill of lading is BL or BoL, it is a legal document that shows the quantity, type, and delivery destination of goods conveyed by a particular carrier. The act of issuing a bill of lading usually takes place between two parties known as the carrier and a shipper.
This means that when goods are to be delivered to a particular destination, either through rail, land, or sea which are the means of transportation. The consignor issues a paper document (Bill of Lading) to the consignee to serve as a shipment receipt.
When this happens, there must be an authoritative signature of the carrier and the shipper because a bill of lading means a contract has been struck between both parties.
Purpose and Importance of Bill of Lading
There are various reasons why the bill of lading is needed during goods transfer. Not only does it show shipment details of a product, but it also helps you identify the goods, identify the consignee’s responsibility, provide proof of shipment, serve as a receipt, and state the payment terms.
In addition, a bill of lading is also used to avoid theft during international trade, and it can rightfully help you claim your goods in case there are complications or mixups during the process of shipment.
Types of Bill of Lading

In the early days, you did not need a bill of lading for all means of shipment, you only needed it if you wanted to ship your products through cargo. Fast forward to today, a bill of lading is applied to other means of logistics like rail and inland freight. Although there are various BoL you need to familiarize yourself with for you to know which category each type falls into. These categories are negotiable or non-negotiable types and carrier responsibility types.
Negotiable and Non-negotiable Bills of Lading

The difference between negotiable and non-negotiable bills of lading is that you change the consignee or cargo ownership in the negotiable BL. This means that you can decide to change the carrier of your goods if you think a particular carrier cannot do the carrying job or will delay your goods.
However, you can only change your goods carrier by properly notifying the carrier. A non-negotiable bill of lading on the other hand is the opposite of a negotiable bill of lading. In this case, it’s clearly stated in the bill of lading the particular carrier to do the job, and it’s not transferable.
1. Consignment Bill of Lading
You can also call them straight bills of lading. They are a type of non-negotiable BoL issued when a customer has already paid a shipping fee.
2. Order Bill of Lading
Order bill of lading is considered the original bill of lading that is used when payment is not made in advance. You can use this type of bill of lading when your shipment is negotiable. They are mostly used to support letters of credit to safely move goods between the buyer and the seller.
3. Charter Party Bill Of Lading
This type of bill of lading is usually used in maritime trade. They are specialized bills of lading used for bulk shipment cargoes to regulate chattering vessels.
In this scenario, a shipper or group of shippers can decide to rent the entire boat to carry the cargo. They are tailored for commodities, and they operate within the framework of a charter party agreement.
4. Switch Party Bill of Lading
A switch party bill of lading is a duplicate BoL issued by the carrier to its agent usually when perishable cargo is to be shipped and it’s the second set of bills of lading passed in this instance.
You cannot alter the port of loading of this type of BoL because the shipper and the carrier are in a contractual agreement. It’s called a switched party bill of lading because the consignee can decide to un-disclose the carrier’s or consignee’s information by telling the carrier to switch the bill of lading.
5. Air Waybill
You can also call Air Waybill a consignment note, dispatch note, or waybill. With this type of bill, you can identify your shipment electronically through its barcode. Not only can you use the barcode to identify your shipments, but you can also use the barcode to track your shipments.
Additionally, they are a standard type of bill that is attached to the outer part of your shipment when the shipment is to be made internationally through air courier services. They’re distributed by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and they are non-negotiable.
Carrier Bills of Lading

The carrier responsibility types of BL show the duties and obligations of the shipper during the cause of moving goods from one place to another. This means that during the cause of shipment, a carrier responsibility bill of lading may indicate that:
- The goods must be transported and delivered the way they are received i.e. no damaged or missing goods.
- The quantity and nature of the goods must be maintained by the shipper,
- The carrier must strictly follow the shipping instructions.
- They’ll be held responsible for any damage or loss when moving the goods to their final destination.
- They must ensure timely delivery of the goods.
NOTE: Sometimes, you may not always find all of this in a single bill of lading. However, this is just to give you an idea of what some carrier responsibilities BL may include.
1. Ocean Bill of Lading
Ocean bill of lading is a document that legally binds the shipper and the carrier of shipment to transport goods across international waters. Additionally, they serve as the receipt and invoice to the shipper by highlighting the description, the quantity, and the routing instructions required for transferring the goods.
2. Inland Bill of Lading
An inland bill of lading is a legal document that binds the shipper and the carrier when goods are to be transported through land. I.e. land or rail. In this case, the BoL is handled over to the carrier instead of sending it to the importer.
3. Master Bill of Lading
A master bill of lading is often used when there are lots of shipments going to the same location. This means that when a shipper has goods from various owners but the goods are going to the same location, a master bill is used instead of having various BLs, and tracking is allowed throughout the shipping process.
4. Direct Bill of Lading
In the case of a direct bill of lading, the vessel that received the cargo will be the one to deliver it to the final destination. This means that there will be no transferring the goods from one vessel to the other.
5. Clean Bill of Lading
A bill of lading is considered clean if goods are loaded in good condition I.e without any record of the damage. After loading, it will be marked as ‘CLEAN ON BOARD”. But this does not mean that the goods loaded in good condition cannot get damaged before they get to their destination. When damage occurs, then the carrier will issue a DIRTY BoL, CLAUSED BoL, or FOUL BoL.
6. Multimodal or Combined Transport Bill of Lading
This type of Bill of lading consists of at least two ways in which you can transport goods i.e. rail, road, or water. Multimodal or combined transport bills of lading are transferable, and the carrier of the goods will be the one responsible for all modes of carriage.
7. Through Bill of Lading
Through bill of lading allows the carrier to move the cargo from one distribution center to another e.g. domestic borders or international shipment. They are more complex due to their various ways of transportation, and they serve as cargo receipts or carriage contracts.
Additionally, This BoL has almost the same function as multimodal or combined transport BoL. The only difference is that in Through BoL if the shipping mode of a product is by rail, you cannot change it to sea.
Non-carrier Bills of Lading
1. House Bill of Lading
A House bill of lading is a negotiable document that is created by an Ocean Transport Intermediary (OTI). This type of BoL is usually given to the supplier when goods have been delivered. The purpose of a house bill of lading is to let the shipper know the goods are delivered.
2. Blank Bill of Lading
A bill of lading is considered a blank BoL if the terms and conditions of carrying a particular shipment are not yet printed on it.
3. Transshipment Bill of Lading
The carrier can transship the cargo to another port to perform his/her duty if the carrier cannot work between two ports. When this is done, the carrier is the one who is responsible for paying for the expense of transhipping.
The Function of The Bill of Lading
There are numerous functions of BoL. Here are some you should familiarize yourself with:
- It shows that the goods have been received by the carrier.
- BoL acts as a title of goods during the cause of shipment.
- It’s a contract that binds the shipper and the carrier when shipping is taking place.
- It’s a document that carries all the necessary information needed for clearance at customs checkpoints.
- It’s a negotiable instrument for financing i.e. you can use them as collateral to secure loans from banks.
Examples of Bills of Lading
The images below showcase some types of bill of lading you should consider familiarizing yourself with.
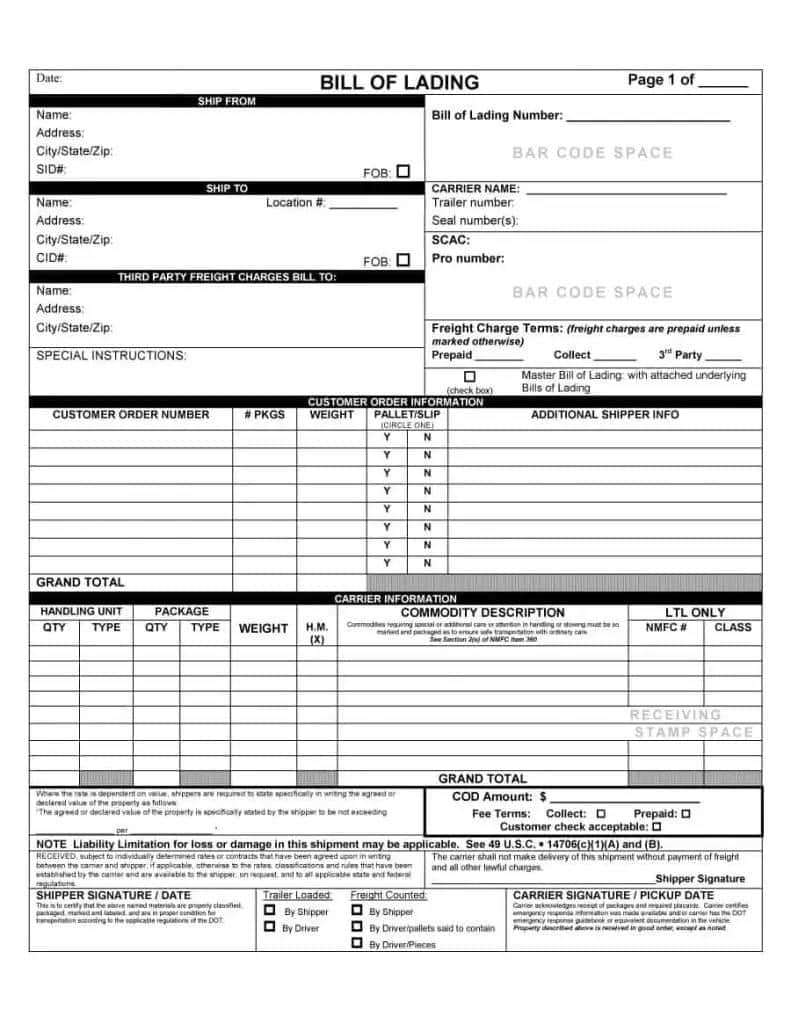

- Shipper: You’ll find the shipper’s personal information, contact details, the name, and the address in the shipper section.
- Consignee: As discussed earlier in the article, the consignee is the one to receive the goods I.e. the trading company or cargo owner.
- Notify Party: The receiver of the goods is the one that receives a notification when the goods arrive at the desired destination.
- Bill Of lading Tracking number: You’ll always find the bill of lading date in this section.
- Voyage/FlightDetails: This section entails information like where the cargo will offload, where the BL issuer responsibilities end, information to track vessel location, the place where the cargo was received by the issuer of the bill of lading or airwaybill and the loading destination of the cargo.
- Cargo Details: Here you will find Information like cargo descriptions, cargo weight, how much load cargo is carrying, the container number, seal no, note that the carrier accepted the goods, and note to identify the goods in the cargo.
- Contract Details: Since the agreement has become legal, you’ll see the issuer’s signature here, freight charges, if any adjustments are made to the bill, weighing, and document negotiations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a bill of lading is one important and legal document required for you to successfully tranship your goods from different cargoes without mixups. Familiarizing yourself with the various types will help you make an informed decision in the process of shipping.
However, you can always trust SourcingWise for your local and international shipping. Our delivery is fast, our cost is very affordable, and you do not have to worry about your goods because you’ll always receive them in good condition.
FAQs
1. What Does a Bill of Lading Entail?
BoL entails the type, quantity, and delivery destination of a particular goods.
2. What Is The Process of Transferring a Bill of Lading?
This process involves two steps which are signing and delivery. The consignee whose name is listed on the bill of lading sign, after which the bill of lading will be delivered to the new recipient.
3. When Can a Bill Of Lading Be Issued?
A Bill of lading is issued after the goods to be shipped are loaded into the vessel.
4. Is The Bill of Lading The Same as an Invoice?
No, a bill of lading is not the same as an invoice. A bill of lading is a receipt of goods conveyed by a carrier. A freight bill is a perfect example of an invoice.
5. Who Is The Consignee in The Bill of Lading?
A consignee is the person that receives the goods when the cargo is released. The name of the consignee is usually written on the BoL to ensure accurate delivery.
6. How Is Logistics Handled By SourcingWise When Doing Business Internationally?
SourcingWise has an outstanding business relationship with trusted logistics companies to make sure your goods are delivered safely to your location.
7. What Is an Original Bill of Lading?
A bill of lading is considered to be original if it serves as the shipment receipt and cargo title.
8. Do All Shipments Have a Bill of Lading?
No, only goods that a carrier transports have a bill of lading.
9. What Are The Charges For Bill Of Lading?
Bill of lading charges are not fixed. The actual charges are usually determined by the carrier.
10. What Happens if The Bill of Lading Has Missing Information?
If there’s missing information, the shipper is penalized for missing information and may be required to pay a sum of money to the carrier.
